How to automate Cloudstack operations with the REST API and IAC platforms
Case
You need to go beyond managing your Cloudstack environment via the Cloudstack portal (https://localhost:8080/client). You need to automate your Cloudstack operations by using the Cloudstack REST API (https://localhost:8080/client/api) and Infrastructure As Code (IaC) platforms, such as Terraform. This article will provide guidance on how to automate Cloudstack operations with the REST API and Infrastructure As Code. Multiple solutions are available, as described in this article.
Solutions
Configuring the Cloudstack API
The following items are required in order to successfully run a REST API call to Cloudstack:
- URL of the CloudStack server you wish to integrate with.
- Both the API Key and Secret Key for a Cloudstack account. This should have been generated by the administrator of the cloud instance and given to you.
- Familiarity with HTTP GET/POST and query strings.
- Knowledge of either XML or JSON.
- Knowledge of a programming language that can generate HTTP requests; for example, Java or PHP.
Generate Cloudstack API public and private keys
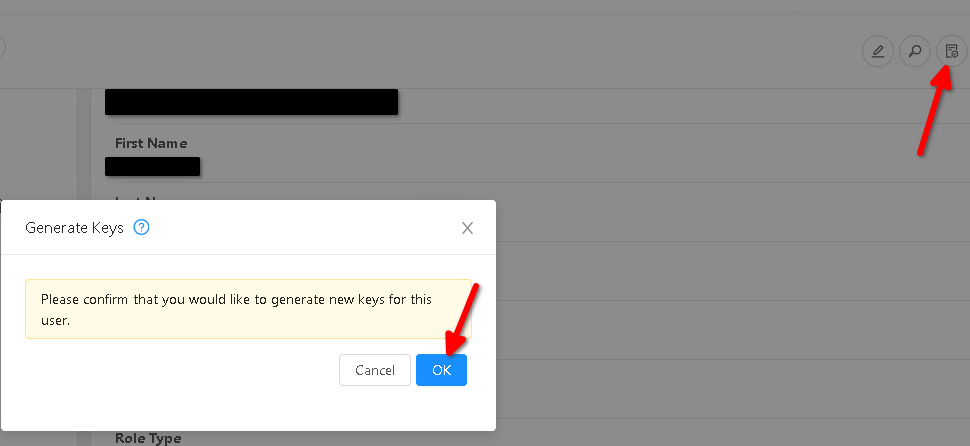
First create a new user/account in the Cloudstack portal. Next, navigate to the user's page and click on the top right hand icon reading "Generate Keys". Click "OK" on the prompt.
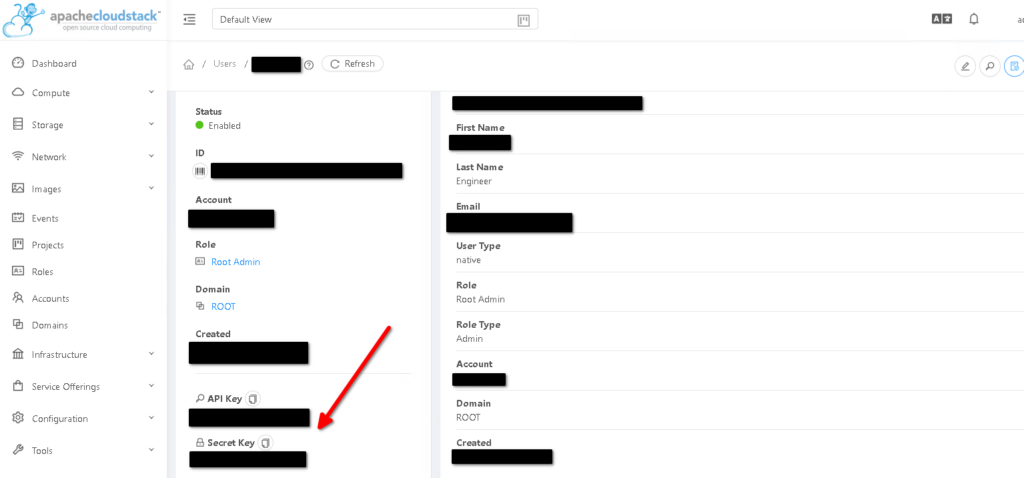
You shall see the generated API key and private key at the bottom of the user's page in the Cloudstack portal.
Generate Cloudstack API signature with Python2
Whether you access the CloudStack API with HTTP or HTTPS, it must still be signed so that CloudStack can verify the caller has been authenticated and authorized to execute the command. Make sure that you have both the API Key and Secret Key provided by the CloudStack administrator for your account before proceeding with the signing process. We will use Python2 in interactive mode to generate the required signature, as shown in the CLI commands below.
python2
import urllib2
import urllib
import hashlib
import hmac
import base64
baseurl=''
request={}
request='listUsers'
request='json'
request=''
secretkey=''
request_str='&'.join()]) for k in request.keys()])
#The below command will test the generation of the API request string
request_str
# Output of above command should be like
# 'apikey=&command=listUsers&response=json'
sig_str='&'.join(.lower().replace('+',''))])for k in sorted(request.iterkeys())])
sig=hmac.new(secretkey,sig_str,hashlib.sha1)
sig=hmac.new(secretkey,sig_str,hashlib.sha1).digest()
sig=base64.encodestring(hmac.new(secretkey,sig_str,hashlib.sha1).digest())
sig=base64.encodestring(hmac.new(secretkey,sig_str,hashlib.sha1).digest()).strip()
sig=urllib.quote_plus(base64.encodestring(hmac.new(secretkey,sig_str,hashlib.sha1).digest()).strip())
#The final sig object holds the signature string
req=baseurl+request_str+'&signature='+sig
res=urllib2.urlopen(req)
res.read()
Automating Cloudstack with Cloudmonkey
To install Cloudmonkey on an Ubuntu machine, run the following commands.
#Option 1: Install from snap
sudo apt update
sudo apt install snapd
sudo snap install cloudmonkey
#Option 2: Install via Python PIP2 (PIP3 has a bug), assumes snap is not present
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python2
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py --output get-pip.py
sudo python2 get-pip.py
sudo pip2 install cloudmonkey
#Option 3 - RECOMMENDED
# Use the latest cloudmonkey (https://github.com/apache/cloudstack-cloudmonkey/releases) which is a complete new re-write in Go. The Python based cloudmonkey won't be maintained anymore.
#This example uses the x64 binaries for Ubuntu Linux
wget https://github.com/apache/cloudstack-cloudmonkey/releases/download/6.2.0/cmk.linux.x86-64
chmod +x cmk.linux.x86-64
sudo mv cmk.linux.x86-64 /bin/cmk
#Run cloudmonkey and setup a new profile
/bin/cmk
set profile poc
set apikey
set secretkey
set domain
set username
set password
sync
Use the following cmk binary command reference from the official apache github repository of Cloudmonkey (CMK).
Cmk will create a new config directory under ~/.cmk.
This allows legacy cloudmonkey to be used as well.
Cmk will store server profile specific API cache in the ~/.cmk/profiles directory.
You should now be able to run cloudmonkey commands as in the example below.
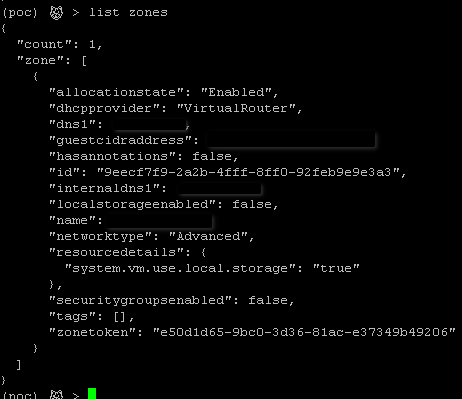
You can choose the output format of Cloudmonkey by setting the corresponding parameter in the command line (XML, JSON, CSV, tabular).
Cloudmonkey commands can also be scripted and then piped to the cloudmonkey executable as in the following example.
cat cmk-script-file
list users
list zones
cloudmonkey < cmk-script-file
More details on Cloudmonkey for Cloudstack operations can be found at:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/CLOUDSTACK/CloudStack+cloudmonkey+CLI
Terraform provider for Cloudstack
You can manage Cloudstack with various IaC platforms such as Terraform. First you will need to install the Terraform runtime on a server accessible to the Cloudstack management server. Run the commands below on an Ubuntu machine, to install the Terraform runtime.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y gnupg software-properties-common curl
curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-add-repository "deb https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main"
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install terraform
#Test that the Terraform engine is working by running a help command
terraform -help
There is a Terraform provider for Cloudstack provided by the Apache Foundation. You will need to have a functional Cloudstack API before implementing the Terraform provider for Cloudstack. Terraform basically requires the creation of a few Terraform configuration and state files (.tf and .tfstate extensions) which will provide declarative programming instructions to Cloudstack to manage resources (create, edit, delete). The following diagram provides an understanding of the high-level architecture of Terraform.
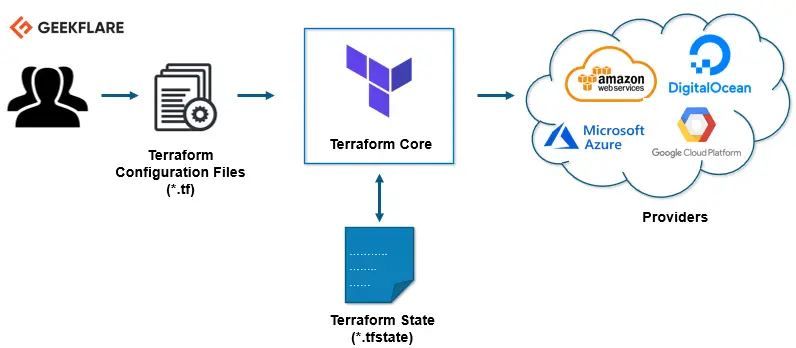
The following Terraform configuration files (.tf) and state files (.tfstate) will need to be created and populated with actual values from your Cloudstack environment. The following sample files provide an example.
main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
cloudstack = {
source = "cloudstack/cloudstack"
version = "0.4.0"
}
}
}
provider "cloudstack" {
# Configuration options
api_url = var.api_url
api_key = var.api_key
secret_key = var.secret_key
}
variable "api_url" {
description = "API URL"
type = string
default = "http://x.x.x.x:8080/client/api"
}
variable "api_key" {
description = "API key"
type = string
default = "XXXXXXX"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key"
type = string
default = "YYYYYYY"
}
cloudstack_network.tf
resource "cloudstack_network" "isolated_net" {
name = "CS_ISOLATED_NET"
cidr = "/24"
network_offering = "DefaultIsolatedNetworkOfferingWithSourceNatService"
zone = "zone01"
}
cloudstack_template.tf
resource "cloudstack_template" "LinuxKVM" {
name = "LinuxKVM"
os_type = "Other Linux (64-bit)"
zone = "zone01"
url = ""
format = "QCOW2"
hypervisor = "KVM"
}
cloudstack_instance.tf
resource "cloudstack_instance" "VirtualMachine01" {
name = "VM01"
service_offering = "Large Instance"
template = cloudstack_template.LinuxKVM.id
network_id = cloudstack_network.isolated_net.id
zone = "zone01"
expunge = true
}
The following Terraform runtime commands can be used to apply the above changes.
terraform init
terraform -install-autocomplete
terraform plan
terraform apply
terraform destroy

After creating the main.tf in the terraform working directory and running the init command, terraform is ready to communicate with your Cloudstack environment.
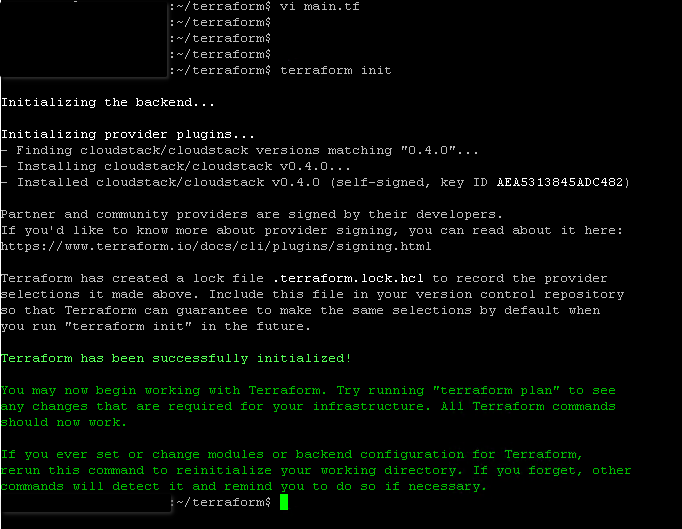
Powershell for Cloudstack
Follow the steps below to use Powershell to automate Cloudstack management tasks.
- Download the Cloudstack API module for Powershell which is available in GitHub at https://github.com/schubergphilis/psCloudstack. Copy the downloaded files into the Powershell default modules folder in your Windows computer. This location is C:UsersDocumentsWindowsPowerShellModulespsCloudstack.
- Configure the Powershell execution policy by running the following cmdlets.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope currentuser
#Import the Cloudstack API module
Import-Module psCloudstack
Add-CSConfig -server -apikey -secret -useSSL -SecurePort 443 -UnsecurePort 80
#Confirm PSCloudStack configuration
get-csconfig
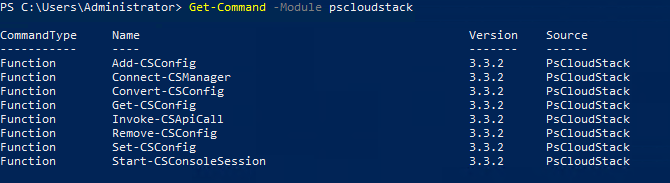
#Receive list of available commands in the module
Get-Command -Module psCloudstack
#Run some test Get commands via the API
Further documentation of the psCloudstack module can be found at: https://github.com/schubergphilis/psCloudstack. Please note that the psCloudstack Powershell module is not actively maintained and it may not work with the most recent versions of Cloudstack.
Saltstack for Cloudstack
Details on how to automate Cloudstack with Saltstack can be found at:
https://docs.saltproject.io/en/latest/ref/clouds/all/salt.cloud.clouds.cloudstack.html
Ansible for Cloudstack
Details on how to automate Cloudstack with Ansible can be found at:
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/scenario_guides/guide_cloudstack.html
Puppet for Cloudstack
Details on how to automate Cloudstack with Puppet can be found at:
https://forge.puppet.com/modules/Lavaburn/cloudstack
Chef for Cloudstack
Details on how to automate Cloudstack with Chef can be found at:
https://supermarket.chef.io/cookbooks/cloudstack
Automating backup and restore of Cloudstack-managed VMs
CloudStack version 4.14 introduces a new Backup and Recovery (B&R) framework which provides CloudStack with users the ability to back up their guest VMs for recovery purposes via third-party backup solutions. The framework abstracts the API commands required for common backup and recovery operations, from the vendor specific commmands needed to perform those actions and provides a plugin model to enable any solution which provides backup and recovery ‘like’ features to be integrated. Currently, the only supported provider is VMware with Veeam Backup and Recovery. Third-party backup vendors can utilize this framework to integrate their solution with Cloudstack for backup and restore automation. More details can be found at: http://docs.cloudstack.apache.org/en/latest/adminguide/backup_and_recovery.html.
Sources
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/CLOUDSTACK/CloudStack+cloudmonkey+CLI
https://github.com/apache/cloudstack-cloudmonkey
https://docs.cloudstack.apache.org/en/latest/developersguide/dev.html
https://geekflare.com/terraform-for-beginners/
https://www.terraform.io/cli/commands
https://learn.hashicorp.com/tutorials/terraform/install-cli
https://github.com/ZConverter-samples/oci_terraform/blob/main/README.md
https://registry.terraform.io/providers/cloudstack/cloudstack/0.4.0
https://github.com/apache/cloudstack-terraform-provider
https://github.com/cloudstack/terraform-provider-cloudstack
https://blogs.apache.org/cloudstack/entry/apache-cloudstack-terraform-provider-v0
https://github.com/ZConverter-samples/oci_terraform/blob/main/README.md
https://www.shapeblue.com/automating-infrastructure-with-cloudstack-and-terraform/
https://kb.leaseweb.com/products/elastic-compute/managing-apache-cloudstack-api-and-automation
https://docs.cloudstack.apache.org/projects/archived-cloudstack-getting-started/en/latest/dev.html
https://stefanos.cloud/kb/how-to-automate-cloudstack-operations-with-the-rest-api-and-iac-platforms/
Comments
Post a Comment